If we want to filter rows based on values within a specific range then we use, BETWEEN operator. BETWEEN Operator is used with AND clause to specify a range of values.
Here’s the syntax for BETWEEN operator in Oracle:
SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name BETWEEN value1 AND value2;
Lets take this table_1 as an example:
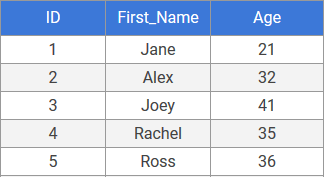
Suppose we want to find people with ages between 25 to 35, we use the following query:
SELECT ID, first_name, age FROM table_1 WHERE age BETWEEN 25 AND 35;
Result:
We will only get those people having age withing the specific range of 25 to 35.

BETWEEN Examples:
1. Oracle BETWEEN with numerical values
Lets take Employees table in the HR schema,
The following query will retrieve employees having salary between the range of 3000 to 7000.
SELECT first_name, salary FROM employees WHERE salary BETWEEN 3000 AND 7000 ORDER BY salary;
Result:
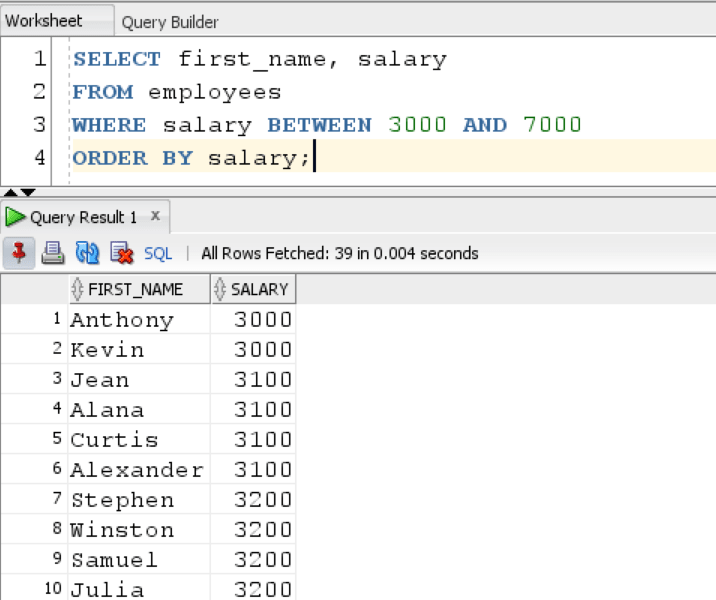
We get all the employees having salary within that range.
Suppose we want to retrieve only those employees who don’t belong in this range then we use the NOT operator and use the following query:
SELECT first_name, salary FROM employees WHERE salary NOT BETWEEN 3000 AND 7000 ORDER BY salary;
Result:
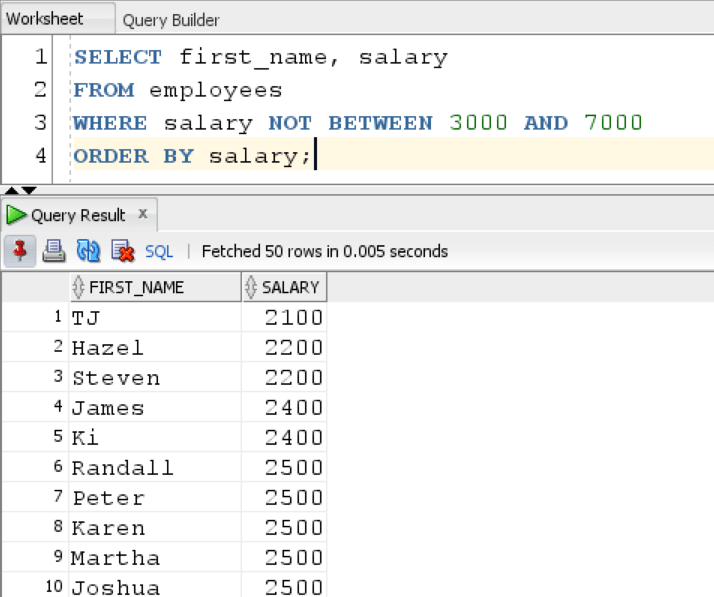
We get all the employees whose salary does not belong in the range of 3000 to 7000.
2. Oracle BETWEEN with dates
Using the same Employee table, lets figure out the employees who were hired before 1996.
We use this query to sort employees based on their hire date:
SELECT first_name, salary FROM employees WHERE hire_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-1993' AND '31-DEC-1996' ;
Result:
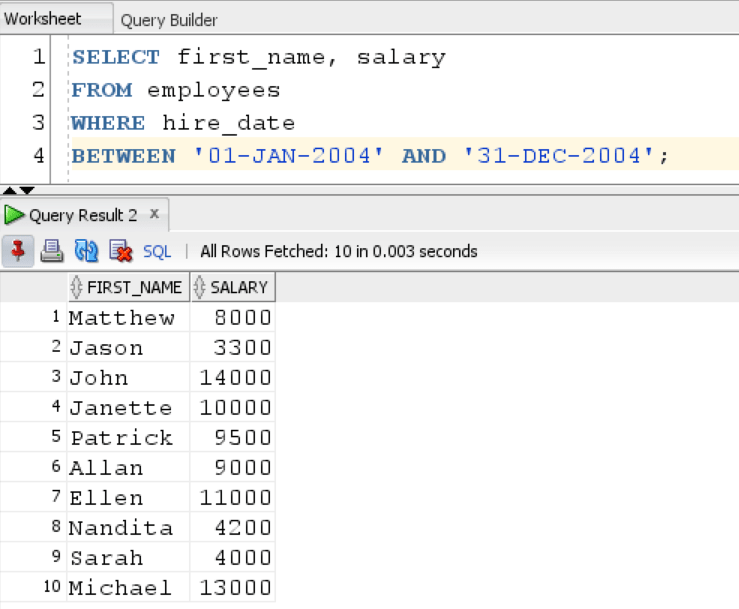
This query will give us all the employees who were hired within that range.
In this article, we learned how to use BETWEEN operator to filter rows based on a range of values.
