When we create an Index on more than one columns in a table, then it is known as Compound Index.
In real life scenarios, often times we need to use more than one columns in a query and if the table contains a lot of rows, the performance of query will be generally slow.
We use Compound Index for optimizing the performance of such queries containing more than one columns.
Syntax
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name(column_1, column_2 ...);
Here,
index_name – Name of Index that we want to create.
table_name – Name of table on which index is created.
column_1, column_2 – Name of Columns on which Index is created in a table.
Let’s understand this through Example.
Oracle Compound Index Example
Suppose, we want to find all interns who are earning more than 7000 and have commission more than 100, then we use this query:
SELECT * FROM intern_table WHERE salary > 7000 AND commission > 100;
Result:
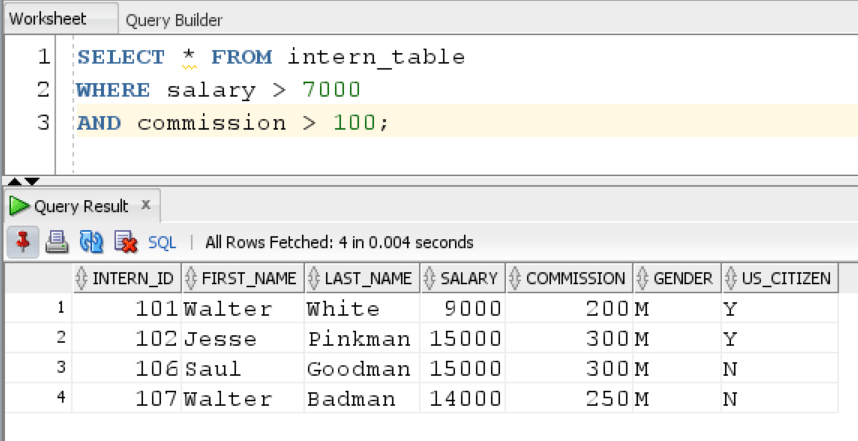
The query returns all interns who are earning more than 7000 and have commission more than 100.
Explain Plan
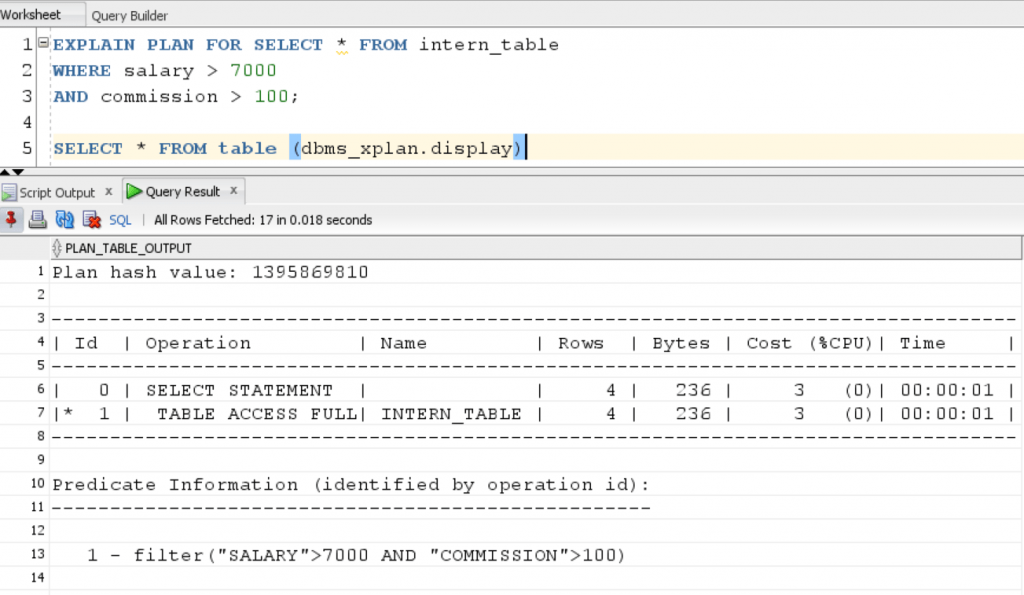
Let’s Explain for this query to understand the execution plan:
EXPLAIN PLAN FOR SELECT * FROM intern_table WHERE salary > 7000 AND commission > 100; SELECT * FROM table (dbms_xplan.display)
Result:
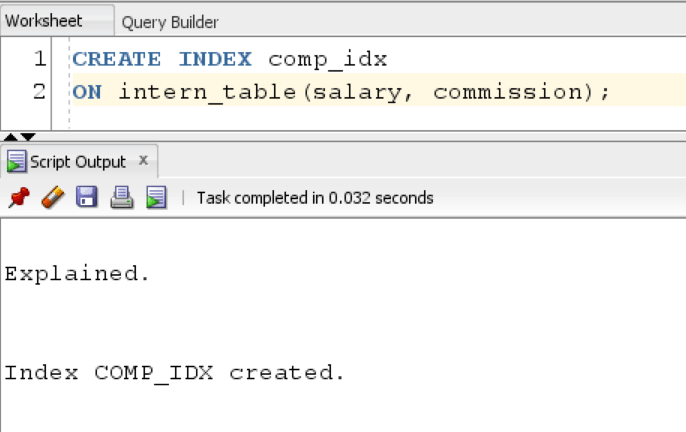
Create Compound Index
CREATE INDEX comp_idx ON intern_table(salary, commission);
Result:
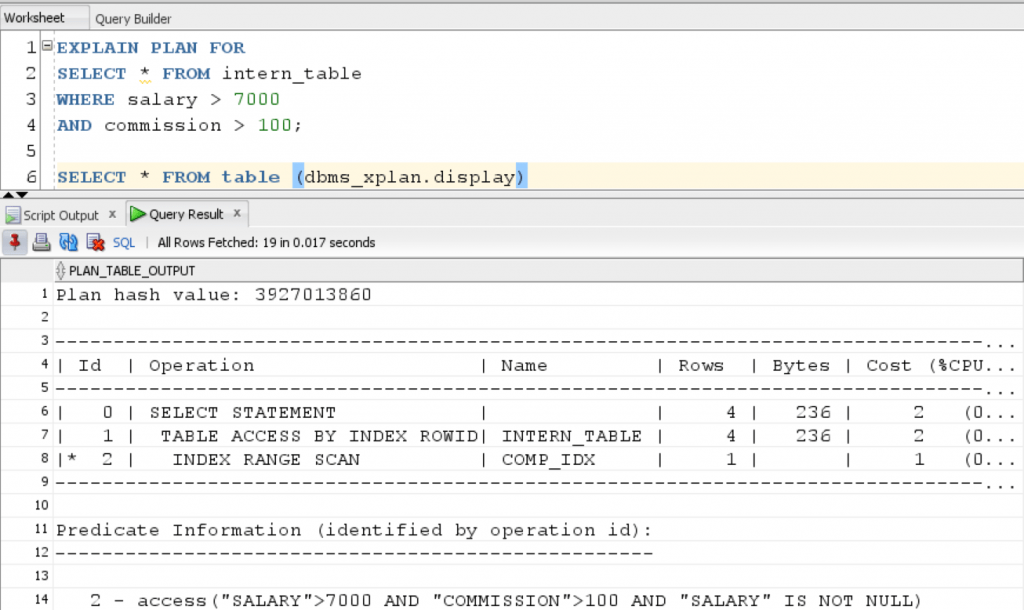
Now, let’s again see the execution plan of above query to see if there is an impact on performance:
EXPLAIN PLAN FOR SELECT * FROM intern_table WHERE salary > 7000 AND commission > 100; SELECT * FROM table (dbms_xplan.display)
Result:
Drop Compound Index
If we want to drop the compound index then we use this query:
DROP INDEX comp_idx;
In this tutorial, we learned about the usage of Compound Index in Oracle and how we can create and drop it in Oracle.
