We have seen UNION, UNION ALL and INTERSECT set operators till now and MINUS is the final set operator in Oracle.
MINUS Set operator is used for returning rows that are present in the first query which are absent in second query.
Syntax:
The syntax of MINUS set operator is as follows:
SELECT
column1, column2, column_n ...
FROM
Table1
MINUS
SELECT
column1, column2, column_n ...
FROM
Table2;Here, column1, column2, column_n.. – List of columns in each table. The number of columns and their order should be same in both first and second query. Also the data type of corresponding columns must be in the same data type group, i.e, numeric or characters.
Table1 and Table2 – The name of tables in first and second query
Let’s revisit the concept of how set operators work in mathematics, before we see examples of MINUS set operator.

Let’s see some examples of MINUS operator.
Oracle MINUS Operator Example
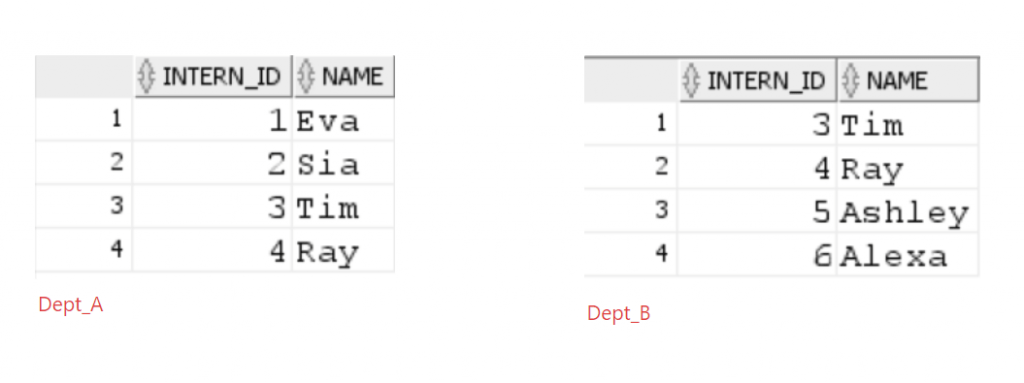
Let’s create two tables named dept_a and dept_b for these examples:
CREATE TABLE dept_a (
intern_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR2 (50) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE dept_b (
intern_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR2 (50) NOT NULL
);
-- insert data in department_a table
INSERT INTO dept_a (intern_id, name)
VALUES (1, 'Eva');
INSERT INTO dept_a (intern_id, name)
VALUES (2, 'Sia');
INSERT INTO dept_a (intern_id, name)
VALUES (3, 'Tim');
INSERT INTO dept_a (intern_id, name)
VALUES (4, 'Ray');
-- insert data in dept_b table
INSERT INTO dept_b (intern_id, name)
VALUES (3, 'Tim');
INSERT INTO dept_b (intern_id, name)
VALUES (4, 'Ray');
INSERT INTO dept_b (intern_id, name)
VALUES (5, 'Ashley');
INSERT INTO dept_b (intern_id, name)
VALUES (6, 'Alexa');Result:
Suppose, we want to see the interns which are present in Department_A but not present in Department_B then we use this query:
SELECT
intern_id,
name
FROM
department_a
MINUS
SELECT
intern_id,
name
FROM
department_b;Result:
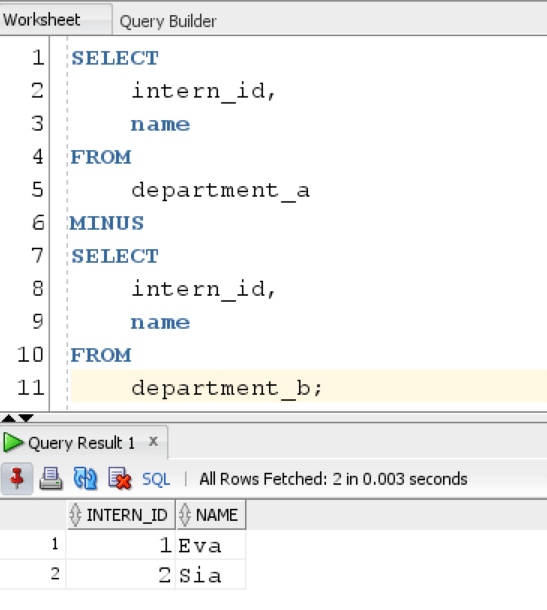
The query returns interns which are unique to department_A.
Suppose we want to flip the result set and only want to see interns which are present in Department_B but not present in department_A, then we use the same minus operator but change the order of first and second query.
SELECT
intern_id,
name
FROM
department_b
MINUS
SELECT
intern_id,
name
FROM
department_a;Result:
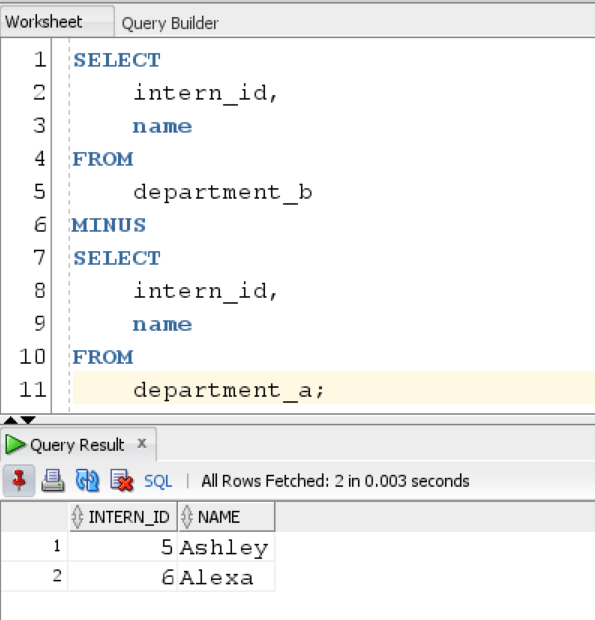
The query returns the list of interns which are only present in Department_B.
In this tutorial, we learned how to use MINUS set operator to find unique values in the result set of either first or second query.
